Cervical cancer: the importance of regular screening
- Dr.Binh Tele_Clinic offers up to 30% off on endoscopy with anesthesia combos
- Special Offers at Dr.Binh Tele_Clinic on Vietnamese Women’s Day
- Dangerous complications of cerebral infarction
- What to know when treating urinary stones?
18/09/2018
-0 Bình luận
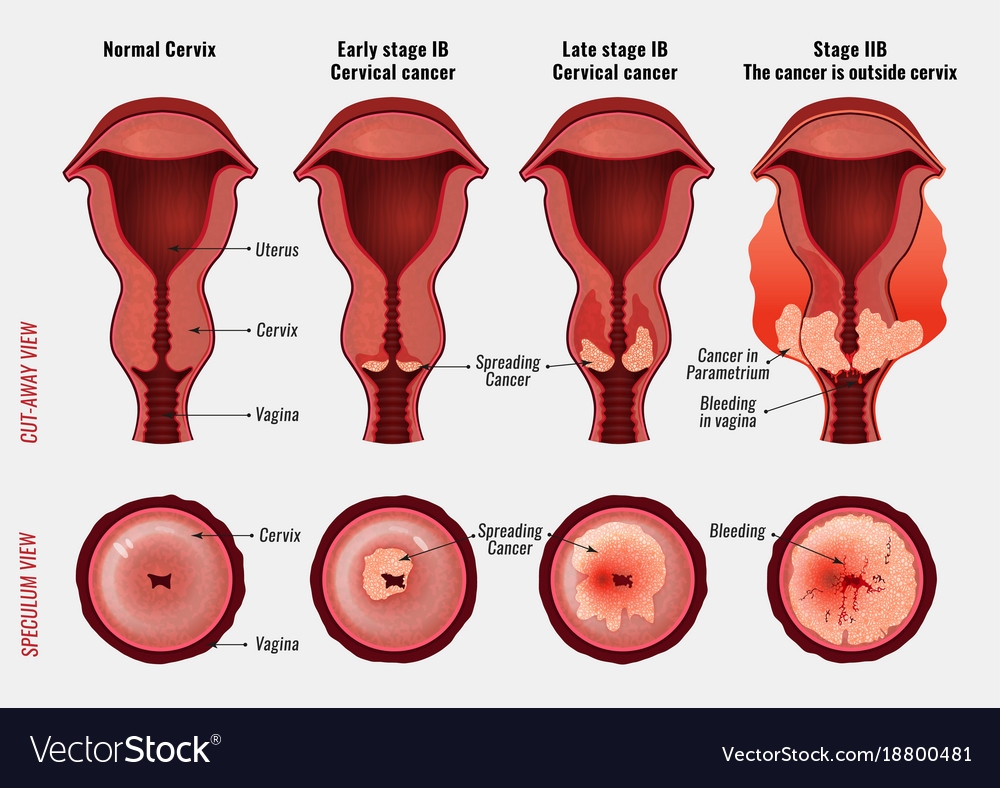
Cervical Cancer Overview
The uterine cervix is the lowest portion of a woman's uterus (womb), connecting the uterus with the vagina.
Cervical cancer occurs when the cells of the cervix grow abnormally and invade other tissues and organs of the body. When it is invasive, this cancer affects the deeper tissues of the cervix and may have spread to other parts of the body (metastasis), most notably the lungs, liver, bladder, vagina, and rectum [1].
Worldwide, cervical cancer is both the second-most common cause of cancer of death in women. In 2012, an estimated 528,000 cases of cervical cancer occurred, with 266,000 deaths. About 70% of cervical cancers occur in developing countries [2]. In developed countries, the widespread use of cervical screening programs has dramatically reduced rates of cervical cancer [3].
The risks for cervical cancer
The National Institutes of Health state that almost all cases of cervical cancer are caused by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV). There are over 100 types of HPV, and around 40 of these can be sexually transmitted. Of these, approximately 15 are thought to be cancer-causing viruses, with two types - HPV-16 and HPV-18 - being responsible for around 70% of cervical cancer cases globally.
Other risk factors include smoking, a weak immune system, birth control pills, starting sex at a young age, and having many sexual partners [4]… because they lead to greater exposure to HPV.
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn't mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to our doctor if you think you may be at risk for cervical cancer.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
Health professionals have referred to cervical cancer as the "silent killer." Spotting cervical cancer in its early stages can prove difficult, you may have no signs or symptoms of cervical canceruntil it has progressed to a dangerous stage. They may include:
- Pain, when the cancer is advanced
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding (other than during menstruation)
- Pain during sex
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Pelvic pain
- Kidney failure due to a urinary tract or bowel obstruction, when the cancer is advanced
Treatment
Cervical cancer treatment options include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or combinations of these.
Deciding on the kind of treatment depends on several factors, such as the stage of the cancer, as well as the patient's age and state of health.
Treatment for early-stage cervical cancer, when it is confined to the cervix, has a good success rate. The further the cancer has spread out of the area it originated from, the lower the success rate tends to be.
Prevention
There are a number of measures that can be taken to reduce the chances of developing cervical cancer.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine
- Safe sex
- Cervical screening
- Having fewer sexual partners
- Delaying first sexual intercourse
- Stopping smoking
The importance of cervical cancer screening
There are two main screening methods for cervical cancer. The first is liquid-based cytology (LBC).
This involves the doctor or nurse scraping the cervix with a small brush to collect cells. The head of this brush is then detached and preserved in liquid, before being sent to a laboratory to be analyzed for cell abnormalities.
The second screening method is the Papanicolaou (Pap) test, also referred to as a cervical smear test. This involves a doctor or nurse scraping the outer opening of the patient's cervix in order to collect a sample of cells. These cells are then analyzed under a microscope for any abnormalities.
Women aged between 30-65 years can choose to have the Pap test every 3 years.
Due to increased usage of the Pap test, the death rate as a result of cervical cancer reduced by almost 70% - meaning the screening may have saved millions of lives [5].
The stage at which cervical cancer is diagnosed can help indicate the chances that a person will survive for at least 5 years more years.
- Stage 1: In early stage 1, the chance of surviving at least 5 years is 93 percent, and in late stage 1, it is 80 percent.
- Stage 2: In early stage 2, the rate is 63 percent, falling to 58 percent by the end of stage 2.
- Stage 3: During this stage, the chances fall from 35 percent to 32 percent.
- Stage 4: There is a 15 to 16 percent chance of surviving another 5 years.
These are average survival rates and do not apply to everyone [6].
Early detection of cervical cancer is the most important factor that helps increase the cure rate as well as reduce medical costs.
This information for guide education and there is no substitute for the visit with the health worker. For more specific and detailed information, please contact: 19009204, post questions here or or go to Dr. Binh Tele_Clinic to be consulted directly by the experienced health worker.
1. Cervical Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, & Outlook, https://www.webmd.com/cancer/cervical-cancer/cervical-cancer#1
2. Stewart, B.W., Wild, C., International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization: World cancer report 2014. (2014)
3. Cervical Cancer - March 1, 2000 - American Academy of Family Physicians, https://web.archive.org/web/20050206141303/http://www.aafp.org/afp/20000301/1369.html
4. Cervical Cancer Treatment, https://www.cancer.gov/types/cervical/patient/cervical-treatment-pdq
5. Cervical cancer: the importance of regular screening, https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/271262.php
6. Cervical cancer: Symptoms, causes, stages, and treatment, https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/159821.php




















Bình luận của bạn